Network Notes: EIGRP
Published: 2018-08-19
Overview
EIGRP is an 'advanced' distance vector routing protocol and is the evolution of IGRP. Originally EIGRP was a Cisco proprietary protocol but in 2013 Cisco announced its intention to make EIGRP on open standard. At the time of writing there is an only informational RFC: RFC7868.
Transport
EIGRP has been assigned protocol number 88 and implements its own reliable transport protocol for delivery of unicast and multicast packets. It does not use TCP or UDP.
Metric
There are 6 K coefficient values used in the EIGRP metric calculation. Bandwidth (K1), load (K2), cumulative delay (K3), reliability (K4), MTU (K5) and extended metrics (K6). There is also a hop count parameter but that is used to prevent routing loops, not for best path selection.
K1-5 + hop count are considered to be the EIGRP classic metrics. EIGRP was further enhanced to support so called wide metrics. Wide metrics accommodate for interface speeds greater than 10G. Additionally the K6 coefficient was added and bandwidth is referred to as throughput while delay is referred to as latency.
Best Path Selection
EIGRP uses the K values to calculate the best path to a destination. All routers in an EIGRP autonomous system should use the same K values to compute the best path. By default only the lowest bandwidth (K1) and cumulative delay (K3) to a destination are used in the best path calculation.
Essentially the default metric is calculated as follows:
(256 x 10⁷ / lowest_bandwidth) + (256 x sum_of_delays)
For reference the full calculation for both classic and wide metrics are below:
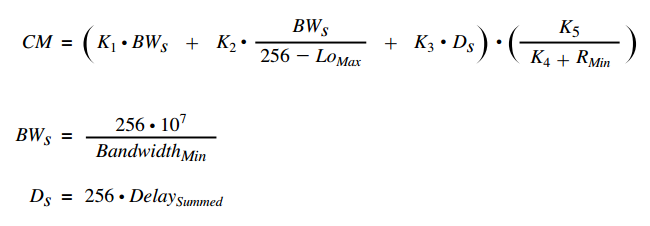
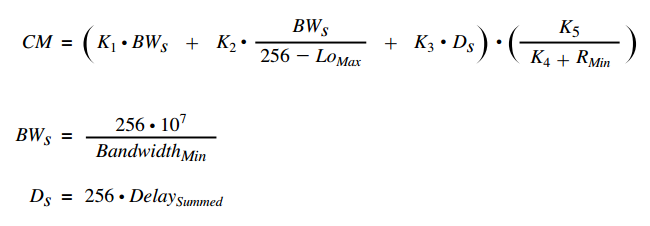
Classic Composite Metric Computation Formula [1]
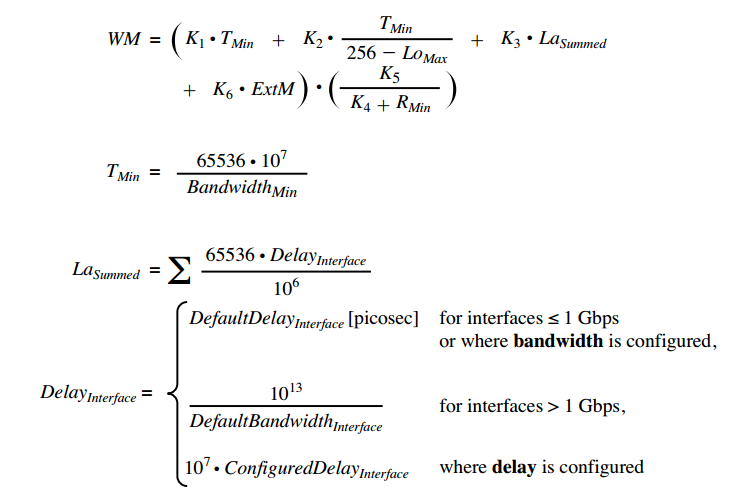

Wide Composite Metric Computation Formula [2]
Neighborship
Neighbor Establishment
For an EIGRP neighborship to be established the following must be true.
- Matching autonomous system number
- Matching K Values
- Matching Multicast (dynamic) or Unicast (static) neighbor configuration
- Matching Authentication Parameters
- Neighbor primary interface IP address resides in a common subnet
Neighbor Packet Types
EIGRP has 7 types of neighbor packets.
Reliable Transport Protocol
Reliable transport protocol (RTP) ensures that EIGRP packets are not only delivered, but also delivered in the correct order. There is no separate RTP packet format, instead RTP is build into the EIGRP messages using sequence numbers and forced acknowledgements. The reliable EIGRP packets types (Update, Query, Reply, SIA-Update and SIA-Reply) must be acknowledged, this ensures the delivery of EIGRP messages.
Diffusing Update Algorithm
Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) is used as the convergence algorithm in EIGRP. DUAL replaces the Bellman-Ford algorithm used in other distance vector protocols. DUAL computes the shortest path using the concept of "diffusing computations" to ensure a loop free topology during the shortest path computation.
Local Computation
During a topology change, if the shortest path provided by a neighbor is already a feasible successor in the topology table the feasible successor is elevated to the successor route without needing to query its neighbors. This is known as a local computation.
Diffusing Computation
During a topology change, if the shortest path provided by a neighbor is not a feasible successor, the router will commence a diffusing computation by sending a Query packet to its neighbors with the prefix and its computed distance to the destination.
DUAL Finite State Machine
The DUAL Finite state machine (FSM) is used to use handle multiple topology changes during a single diffusing computation.
DUAL uses the following parameters in the diffusing computation.
Topology Table
EIGRP stores all its routing information in the topology table. EIGRP will perform a feasibility condition check on routes received by a neighbor to confirm that neighbor can provide a loop free path to the destination. Routes that satisfy the feasibility condition may be installed in the routing table.
Any loop free path to a destination will be installed in the topology table as one of two types of routes.


Route States
Routes in the topology table go through a number of states.
Packet Format
Basic EIGRP message format


Routing Updates
EIGRP exchanges a full routing table when a neighborship is initially established with only partial updates exchanged after that. For a router to accept routing updates from a neighbor the router-id must be different to its local router-id.
Summarization
EIGRP is a classless routing protocol and can summarize networks at any bit boundary.
Loop Prevention
Authentication
EIGRP supports both MD5 and SHA-256 authentication. SHA-256 is only available in EIGRP named mode.
Packet Captures
Various EIGRP PCAPs can be found here.